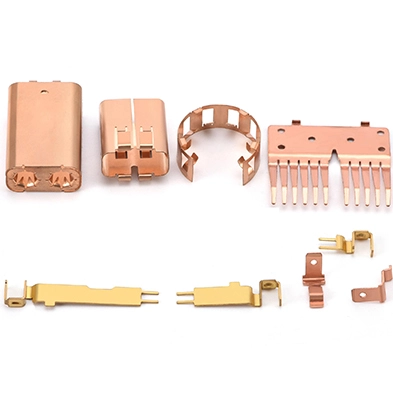
Bending Parts
Edge Rolling Parts
Fine Blanking Parts
Deep Drawing Parts
Copper Stamping
Stainless Steel Stamping
Steel Stamping
Aluminum Stamping
Assembling Service
CNC Machining
Plastic Injection Molding
Electroplating
Other Surface Treatment
Automatic Tapping
Automatic Riveting
Aerospace
Automotive
Electrical And Electronic Accessory
Optical Fiber Communication
Medical Device
Energy Development
Search
 English
English